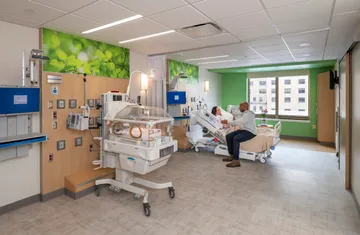
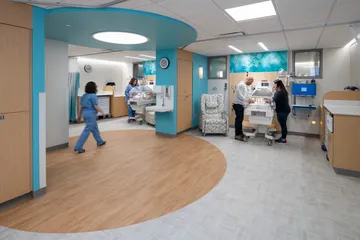
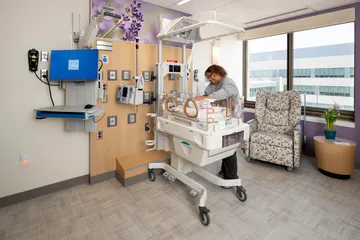
With the nationwide trend of increasing premature births, HSHS St. John’s Children’s Hospital needed to make drastic changes to their existing 45-bed, 15,000-sq.ft. Level III NICU. At the outset, project leaders knew they wanted to build upon the latest evidence-based design learnings from other best-in-class facilities. The design team and clinicians visited multiple benchmark facilities where they collaborated with staff and leadership, better understanding lessons learned and best practices.
Kahler Slater, the clinical design team, and women and children’s healthcare experts, Smith Hager Bajo, targeted multiple patient outcomes that could be improved with the new environment, including average length of stay and rate of readmission. Phase I of the expanded NICU more than doubles the original size. Innovative features of the expanded program include dedicated NICU rooms for twins, tiny baby sub-unit dedicated to the highly specialized needs of the smallest patients, milk lab where milk technicians can fortify mothers’ breastmilk with additional nutrients and dedicated family respite lounge and overnight sleep suites. They also have the unique offering of couplet care as one of only a few hospitals in the nation offering this innovative program. It allows mom and their NICU baby to stay in the same room, establishing the essential parent-child bond from the outset. Positive outcomes as a result of couplet care have proven to be decreases in length-of-stay and infant morbidity. Couplet care also supports earlier bonding of NICU infant and mother due to earlier skin-to-skin contact and increased breastfeeding success.